SpaceX’s Genius Solution to Build Gravity Starship Space Station, Better than NASA ISS, China’s: Humanity is standing at the edge of a new era in space exploration. For decades, orbital habitats like the International Space Station (ISS) and China’s Tiangong Space Station have defined what it means to live and work beyond Earth. But the future will not stop there. A new race is unfolding—one focused not just on surviving in orbit, but on building a true home for humanity in space.
As new contenders like Axiom Space, Orbital Reef, Vast, and Starlab prepare to enter the orbital arena, one name might seem strangely absent at first glance: SpaceX. Yet appearances are deceiving. Rather than competing with conventional designs, SpaceX is pursuing something far more ambitious—a revolutionary artificial gravity space station built using Starship.
This concept does more than challenge the ISS. It has the potential to redefine space habitation entirely.
The New Space Station Race: Beyond the ISS
For more than two decades, the ISS has served as humanity’s orbital laboratory. It has delivered groundbreaking research, international cooperation, and invaluable experience in long-duration missions. However, it also comes with serious limitations:
- High construction and maintenance costs
- Microgravity health challenges
- Limited internal volume
- Complex, fragile modular assembly
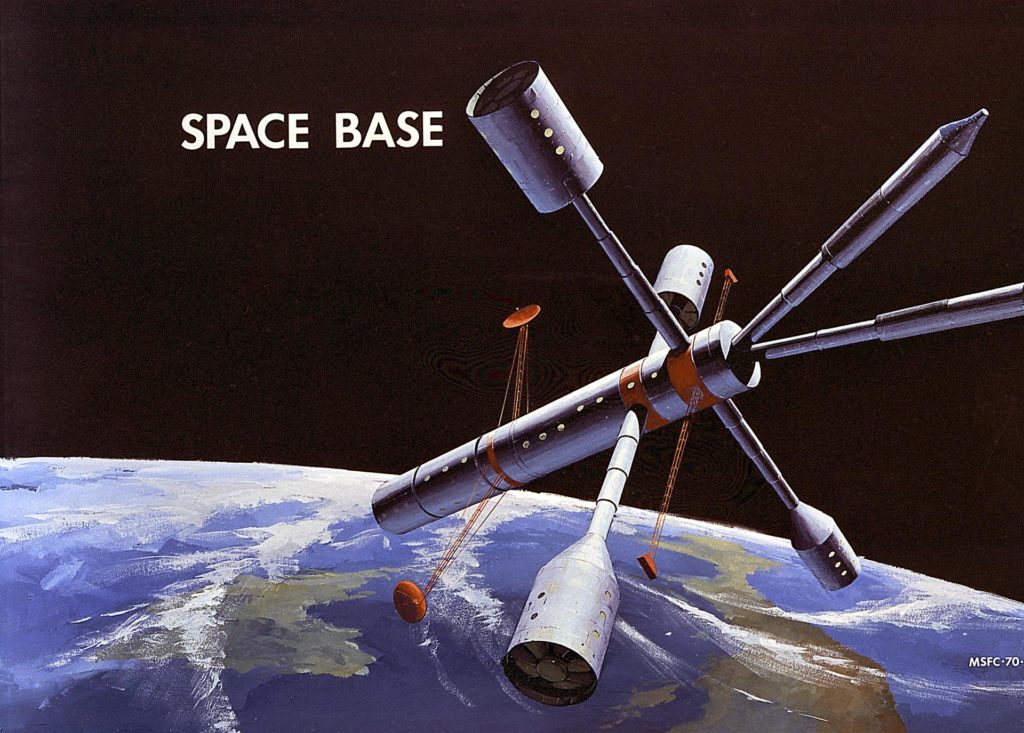
China’s Tiangong station represents a newer approach, but it still relies on traditional zero-gravity architecture and incremental upgrades.
The next generation of stations aims to go further—larger, cheaper, scalable, and capable of supporting long-term human life. This is where SpaceX enters the picture with a bold idea that only it can realistically execute.
Starship: The Foundation of SpaceX’s Orbital Vision
SpaceX’s Starship is already reshaping aerospace history. Designed as a fully reusable super-heavy launch system, Starship is unlike anything humanity has ever built.
Why Starship Changes Everything
Starship is designed to deliver:
- Unprecedented payload capacity
- Extremely low cost per launch
- Rapid launch cadence
- Full reusability
- Interplanetary capability
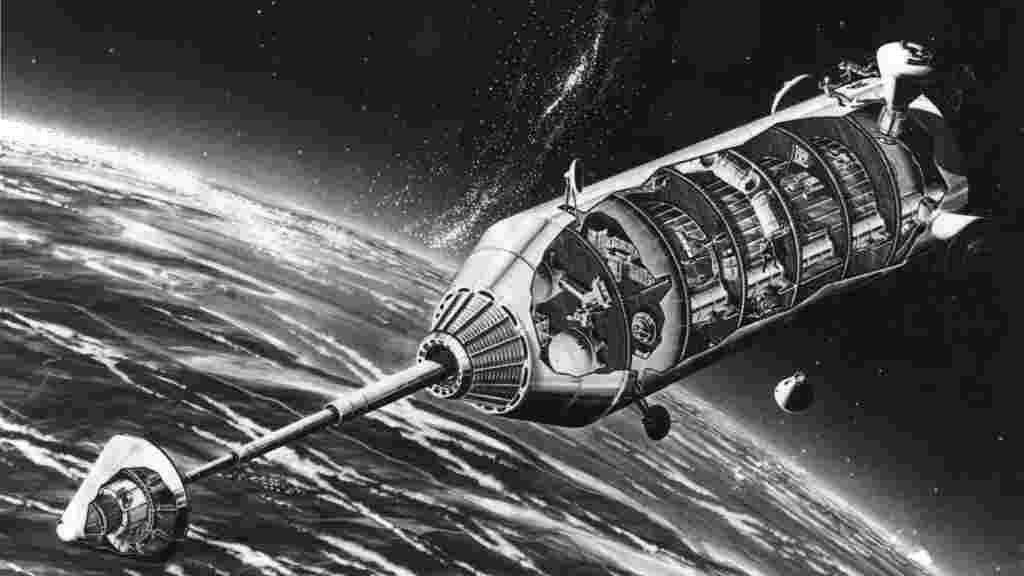
Its scale alone is extraordinary. The upper stage of Starship stands nearly 50 meters tall and 9 meters wide, with future variants reaching 61 meters in height. This immense size opens the door to an entirely new possibility: using Starship itself as a space station module.
And yes—this idea is not science fiction. It is absolutely feasible.
Can Starship Really Become a Space Station?
From an engineering perspective, converting Starship into a space station is surprisingly straightforward.
How a Starship Station Would Work
- Starship would launch normally into orbit
- Instead of returning to Earth, it would remain in permanent orbit
- A custom thruster system would maintain orbital stability
- Life support, habitation systems, and interiors would be fully installed on Earth
- Once deployed, it would function just like a traditional space station—only vastly larger
In fact, human-rating Starship for long-duration missions already requires many of these systems, meaning the leap to a station module is smaller than it appears.

The Numbers That Make Starship Unstoppable
Let’s look at the raw math—because this is where Starship truly dominates.
Internal Volume Comparison
- ISS total pressurized volume: ~1,000 cubic meters
- Single Starship (habitable section only): ~1,100–1,200 cubic meters
- Upgraded Starship station variant:
- V3 (52 m): ~3,300 cubic meters
- V4 (61 m): ~3,800 cubic meters
This means one Starship alone could exceed the entire ISS in internal volume. And SpaceX wouldn’t stop at one.
A Multi-Starship Megastructure in Orbit
Instead of assembling dozens of tiny modules like the ISS, SpaceX could deploy entire Starships as station segments.
A Scalable Orbital City
- Multiple Starships connected together
- Dedicated modules for habitation, research, agriculture, and recreation
- Entire Starships assigned to single purposes
- Continuous expansion over time
This approach allows for growth, upgrades, and redundancy at a scale never before possible in orbit.
The Game-Changer: Artificial Gravity
The most revolutionary aspect of SpaceX’s Starship station concept is not its size—it’s artificial gravity.
Why Microgravity Is a Problem
Living in zero gravity causes:
- Bone density loss
- Muscle atrophy
- Cardiovascular strain
- Vision problems
- Long-term health risks
These effects worsen the longer astronauts stay in space, making permanent habitation extremely difficult.
How a Rotating Starship Station Solves Gravity
SpaceX’s proposed solution involves a rotating orbital structure.
The Rotating Wheel Design
- A central hub acts as the station’s core
- Multiple Starships are arranged in a circular formation
- Radial connections link each Starship to the hub
- The entire system rotates, generating centrifugal force
- This force mimics gravity at 0.3g to 1g, depending on speed and radius
Because Starship is so large, the station’s diameter can be enormous—allowing for slow, stable rotation that avoids motion sickness.

Elon Musk Confirms the Vision
This isn’t just speculation. Elon Musk himself has discussed rotational gravity.
He has stated:
“Starship will have a small spin on the way to Mars. Even a tiny gravity vector is better than none.”
Scaling this idea into a full orbital station could eliminate one of the greatest barriers to long-term space living.
Life with Artificial Gravity in Orbit
Restoring gravity changes everything.
Health Benefits
- Reduced bone and muscle loss
- Improved cardiovascular health
- Longer mission durations
- Fewer crew rotation flights
- Lower long-term costs
Daily Life Becomes Normal
With gravity, astronauts could:
- Walk normally
- Eat without restraints
- Shower more easily
- Use conventional bathrooms
- Sleep in familiar orientations
This dramatically improves mental health, comfort, and productivity.
Inside a Starship Space Station: A New Way of Living
Starship’s massive internal volume allows SpaceX to design interiors that feel far more like Earth-based habitats.
Lower Levels: Storage and Utilities
At the base of each module:
- Maintenance tools and spare parts
- Scientific instruments
- Cargo storage
- Electrical systems
- Water recycling infrastructure
- Power distribution units
This area forms the technical backbone of the station.
Dining and Food Production Areas
Above the utility level lies the communal dining zone.
Key Features
- Shared dining spaces
- Social gathering areas
- Hydroponic and aeroponic gardens
- Fresh food production
- Psychological benefits of plant care
These gardens reduce reliance on resupply missions while improving crew morale.
Fitness and Hygiene Zones
Even with gravity, exercise remains essential.
This level would include:
- Weight machines
- Treadmills
- Rowing stations
- Pull-up systems
- Nearby bathrooms and hygiene facilities
Daily routines become efficient, intuitive, and familiar.

Private Sleeping Quarters
Each astronaut would have a personal cabin, offering:
- Privacy
- Sound insulation
- Personal storage
- Communication systems
- A calming environment for rest
These quarters resemble compact bedrooms, not sleeping bags strapped to walls.
Communal Living and Observation Decks
Near the nose of the Starship:
- Large observation windows
- Earth and space viewing areas
- Team collaboration spaces
- Visual research stations
This area reinforces the human connection to Earth and the awe of space.
Command and Control Center
At the top of the module sits the central operations hub:
- Navigation systems
- Communications equipment
- Station diagnostics
- Mission planning rooms
- Research coordination spaces
This level serves as the brain of the station.
Beyond a Single Module: A True Orbital City
When multiple Starships are combined:
- Entire modules dedicated to research
- Separate agricultural Starships
- Recreation-focused habitats
- Operations-only control units
This transforms the station into a fully functional orbital settlement, not just a laboratory.
Economic Advantages Over Traditional Stations
Traditional space stations are incredibly expensive due to:
- Custom-built components
- Exotic materials
- Disposable launch vehicles
Starship changes this equation completely.
Why Starship Is Cheaper
- Stainless steel construction
- Mass production
- Full reusability
- High launch frequency
- Lower cost per kilogram to orbit
This makes scalable growth and long-term upgrades economically viable.
The Engineering Challenges Ahead
Of course, this vision is not without obstacles.
Key Challenges
- Massive construction effort
- Complex orbital assembly
- Powerful thrusters for initial spin-up
- Maintaining rotational stability
- Long-term structural stresses
Yet none of these challenges are unsolvable—and SpaceX has a proven track record of tackling the impossible.
A Giant Leap Toward Humanity’s Future in Space
A Starship-based artificial gravity space station would represent:
- The end of purely microgravity living
- The beginning of long-term orbital habitation
- A stepping stone to Moon and Mars settlements
- A true space-based civilization hub
It would be bigger, healthier, cheaper, and more human-friendly than anything ever built in orbit.
Final Thoughts
SpaceX’s Starship gravity space station concept is more than an upgrade to the ISS—it’s a complete reimagining of life in space. By combining immense scale, reusable technology, and artificial gravity, SpaceX could finally make space feel like a place where humans truly belong.
If this vision becomes reality, the question will no longer be whether humans can live in space—but how many will call it home.
Curiosity, imagination, and inspiration will always follow those who keep looking up.
FAQs
1. What is SpaceX’s Starship gravity space station?
SpaceX’s Starship gravity space station is a proposed orbital habitat built using Starship vehicles as station modules, potentially arranged in a rotating structure to create artificial gravity for long-term human living in space.
2. How is this station different from the ISS?
Unlike the International Space Station, the Starship-based station would be much larger, cheaper to build, scalable, and capable of producing artificial gravity, reducing health risks associated with long-term microgravity exposure.
3. Can Starship really function as a space station module?
Yes. Starship can be outfitted on Earth with life support, habitation systems, and interior structures, then launched into orbit and repurposed as a long-term station module.
4. How much internal space does a single Starship provide?
A single Starship could offer 1,100–1,200 cubic meters of usable volume, already comparable to or exceeding the total internal volume of the ISS.
5. How big could a full Starship-based space station become?
With multiple Starships connected together, the total pressurized volume could reach tens of thousands of cubic meters, far surpassing any space station ever built.
6. What is artificial gravity and why is it important?
Artificial gravity is created by rotation, using centrifugal force to mimic gravity. It helps prevent bone loss, muscle atrophy, and cardiovascular issues caused by long-term exposure to microgravity.
7. How would artificial gravity be generated on the station?
The station would rotate around a central hub, with Starships arranged in a circular pattern. The rotation produces centrifugal force, simulating gravity levels between 0.3g and 1g.
8. Would astronauts feel motion sickness from rotation?
Because Starship is extremely large, the station could rotate slowly and smoothly, significantly reducing the risk of motion sickness compared to smaller rotating habitats.
9. Has Elon Musk confirmed plans for artificial gravity?
Elon Musk has stated that Starship will use rotational gravity during long-duration missions, suggesting that artificial gravity is a serious and realistic concept for SpaceX.
10. How many astronauts could live on a Starship space station?
Depending on configuration, a single module could support dozens of astronauts, while a full multi-Starship station could house hundreds of long-term residents.
11. What would daily life be like on the station?
With artificial gravity, astronauts could walk normally, exercise naturally, eat without restraints, and sleep in regular beds, making life in space far more comfortable and familiar.
12. Would food be grown on the station?
Yes. The station could include hydroponic and aeroponic gardens, allowing astronauts to grow fresh produce and reduce reliance on Earth resupply missions.
13. How does Starship reduce the cost of space stations?
Starship uses stainless steel, mass production, and full reusability, dramatically lowering construction and launch costs compared to traditional, disposable space station modules.
14. Is this station meant only for Earth orbit?
Initially, yes. However, the same Starship station concept could later be adapted for lunar orbit, Mars transit habitats, or deep-space missions.
15. What scientific research would benefit from artificial gravity?
Artificial gravity enables more predictable biological experiments, long-term medical studies, and research that is impossible in microgravity environments.
16. What are the biggest technical challenges?
Major challenges include assembling large structures in orbit, initiating and maintaining rotation, managing structural stresses, and ensuring long-term system reliability.
17. When could a Starship gravity station become reality?
There is no official timeline, but such a station would likely follow successful Starship operational flights and human-rated missions, potentially in the 2030s.
18. Could civilians or tourists live on the station?
In the long term, yes. The station could support commercial astronauts, researchers, and space tourists, opening the door to permanent human presence in orbit.
19. Why is this concept important for humanity’s future?
A Starship gravity space station could be the first true space habitat, enabling long-term living, supporting planetary exploration, and marking a major step toward becoming a multi-planetary species.
Read More:
- Ford cancels all-electric F-150 Lightning, announces $19.5 billion in charges
- Tesla stands to gain from Ford’s decision to ditch large EVs
- Tesla Cybertruck earns IIHS Top Safety Pick+ award
- Tesla Model Y L is gaining momentum in China’s premium segment
- Tesla gets bold Robotaxi prediction from Wall Street firm

1 thought on “SpaceX’s Genius Solution to Build Gravity Starship Space Station, Better than NASA ISS, China’s”